Economic sphere in the boiling great power relations
As you have seen, my website www.greatpowerrelations.com is focused on the relations of great powers after the Cold War. Those three great powers – the US, China, Russia – their mutual relations as well as their triangle game have been a pivotal research area.
Some of the latest articles under this topic are “Great Powers and Hot Spots” of September 3, 2024; World order and polarity transforming 2022 , February 28, 2022; Cyclical transformation turning into doomsday , March 21, 2022 ; New World Order in the making , April 2, 2022. It appears now, that the situation is very near to “the point of boiling over”.
General features of great power competition
Competition between great powers continues fiercely, in all spheres – political, economic and military. Here we focus on economic affairs as well some occurrences around.
Majority of western “experts and researchers” see that the global order is witnessing a revival of great power competition in the twenty-first century but with China and the United States emerging as the main players. This change represents the shift from the US-dominated post-Cold War era of unipolarity to a more complicated and contentious international system.
They fail to see the development of “Two Camps”. As stated before (my article of Sept 3), the humanity seems to be divided in two camps:
The Western Camp, “Axes of US Empire” (the US and its allies Canada, EU and other West Europe, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, South Korea) and The Eastern Camp, “Axes of Resistance” led by China and Russia and their close allies Iran and North Korea, CIS and CSTO countries, covering majority of Asia, Africa and South America, so called “Global South”.
The eastern group consists of the majority of humanity, both in terms of countries and people. The ratio is six billion people in the east and to one billion in the west. No doubt, which camp will prevail. The leadership will shift to the east and remain there well into the next century.
The international system is undergoing a dramatic shift from an American-dominated unipolar world to a more intricate and sophisticated multipolar order. The establishment of several centres of power, each with influence over various spheres of global governance, characterize this change. Although the focus of talks on world politics is frequently on the role of great powers like the US, China and Russia, middle-powers are becoming more important in forming this changing multipolar landscape.
Middle powers are countries with considerable regional influence and a well-established presence in international diplomacy but lacking the comprehensive force projection capabilities of great powers. These nations frequently possess highly developed economies, intricate diplomatic networks and military might adequate to affect the dynamics of regional security. Middle-power nations may include South Africa, Brazil, Australia, Canada, Mexico, Indonesia and Turkey.
One of the key things that sets middle powers apart is their strategic autonomy. Middle powers frequently conduct autonomous foreign policies that represent their national interests and regional priorities, in contrast to smaller states, which may closely align with superpowers for security and economic reasons. This is the reason why Japan and South Korea are not included in the list of middle powers.
The role of middle powers is growing in importance as the world order continues to shift towards multipolarity. These countries are vital to the stability and smooth operation of the international system because of their strategic independence, dedication to multilateralism, economic might, and contributions to international security.
Economic features of great power competition
My previous overviews on economies of great powers were
“Economic positions of great powers in Spring 2024” on April 26, 2024 and
“Glimpses in economic dimension of current great power competition , on December 10, 2023
A lot of interesting new events and trajectories have emerged since then. So, let’s take a look at the current situation.
Gold
Top 10 countries by gold reserves in 2024 and top 10 countries by the change in gold reserves over the past decade (2013-2023).
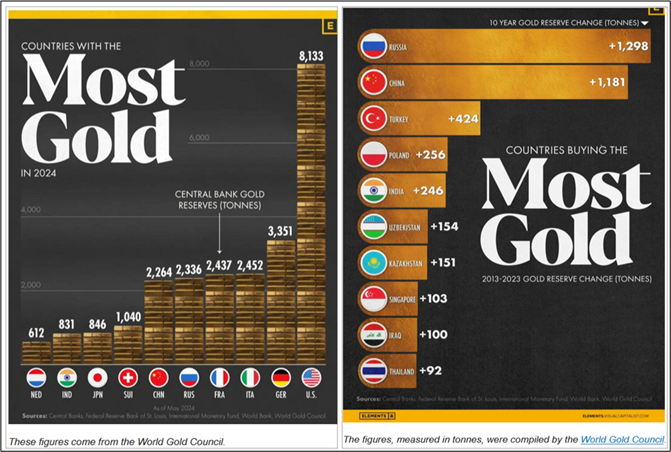
Central banks hold gold reserves due to their safety, liquidity and return characteristics. They are significant owners of gold, accounting for approximately a fifth of all the gold mined throughout history.
Russia and China lead in gold purchases. Central banks, particularly those of Russia and China, have bought gold at the fastest pace as countries seek to diversify their reserves away from the dollar. Russia’s reserves jumped from 1,035 tonnes in 2013 to 2,333 in 2023. China’s reserves rose from 1,054 tonnes to 2,235 in 2023. In third place in our ranking of central bank gold additions, Türkiye increased its reserves from 116 tonnes in 2013 to 540 tonnes in 2023.
Debt
Widespread debt hell plagues, not only developing nations but especially the entire western market economy region as well. As professor Daniel Lacalle put it aptly: “There is no escape from debt.”
Global money supply has soared by $20.6 trillion since 2019, according to Bloomberg. Additionally, global debt surged by over $15 trillion in 2023, reaching a new record high of $313 trillion. Around 55% of this rise came from developed economies, mainly the US, France and Germany. Unfunded liabilities in the United States amount to $72 trillion, almost 300% of GDP. This may seem high until you look at Spain with 500% of GDP, France with close to 400%, or Germany with close to 350% of GDP.
There is no escape from debt. Paying for the government’s fictitious promises in paper money will result in a constantly depreciating currency, thereby impoverishing those who earn a wage or have savings. Inflation is the hidden tax and it is very convenient for governments, because they always blame shops or businesses and present themselves as the solution by printing even more currency.
Governments want more inflation to reduce the impact of the enormous debt and unfunded liabilities in real terms. They know they can’t tax you more, so they will tax you indirectly by destroying the purchasing power of the currency they issue.
In 2024, the world has seen more than seventy elections, where none of the parties with access to power even bothered to present a realistic plan to cut debt. Naturally, currency debasement leads to widespread impoverishment.
The Treasury expects a $16 trillion increase in public debt between 2024 and 2034, without taking into account any recession risk. The enormous government debt of $35 trillion, along with its subsequent additions, has the potential to destroy the currency. Citizens will face higher debt, reduced access to goods and services, and the ultimate dissolution of the middle class in the absence of a pro-growth plan and serious support for the currency’s purchasing power.
The reader who is interested in this topic (debt/banking) I recommend reading this article and see videos below: The Shadow Money System That Rules the World , Keith Woods • July 15, 2024
Banking Crisis Ahead: What This Means for Market Volatility
All Wealthion Videos, July 18, 2024
All Wealthion Videos, July 19, 2024
Stock Market Crash Uncovered: What Really Went Down?
GoldCore TV, August 8, 2024
Gold: The Ultimate Hedge Against Soaring U.S. Debt | Rick Rule
All Wealthion Videos, August 22, 2024
The EU in the framework of great power competition
The EU is a curious entity on the international scene, thus far economically strong union, setup of many militarily quite potential countries but politically and organizationally scattered and divided entity, striving for unrealistic global goals like human-caused climate change hoax, failed energy and industry policies and societal freedom and liberty policy based on “Orwellian ideology” and extreme woke-culture, totally forgetting its own wide cultural heritage.
EU is living in a strange political-military symbiosis with the NATO and both entities under the complete vassalage of the US. This is particularly true now as the Democrats and Biden are leading the US and the European ideological and political life seem to be completely saturated with American-based woke ideology. It appears that the European Union morphs into NATO’s financial war machine and European Parliament is becoming a war council.
As a grotesque example of entirely failed concept of human society and freedom of speech, a Polish MEP tries to speak critically but was cut shortly. Listen this “European Democracy and Freedom of Speech”. This is a caricature of modern liberal society, which day by day is resembling more and more Orwellian horror society, headed by von der Great Liar.
The European Union does not worry a small nuclear war in Europe. “The European Union is not changing its position on the issue of supporting Ukraine due to the words of Russian President Vladimir Putin about updating Russia’s nuclear doctrine,” said EU Foreign Service spokesman Peter Stano.
The EU’s dismissal of Russia’s nuclear doctrine is not just careless—it is deeply irresponsible. Downplaying such a serious issue doesn’t make the threat disappear and pretending that it does only escalates tensions further. Ignoring or dismissing such risks only increases the potential for catastrophic miscalculation.
Climate hoax was revealed by a scientific article in the Washington Post. However, the EU Commission is suicidally striving for those flawed, biased and destructive climate goals, based on that hoax.
Germany, which has been a locomotive of the European economy, has destroyed her industry, energy management and societal cohesion by insane green energy projects based on climate hoax and reckless and uncontrollable migration policy.
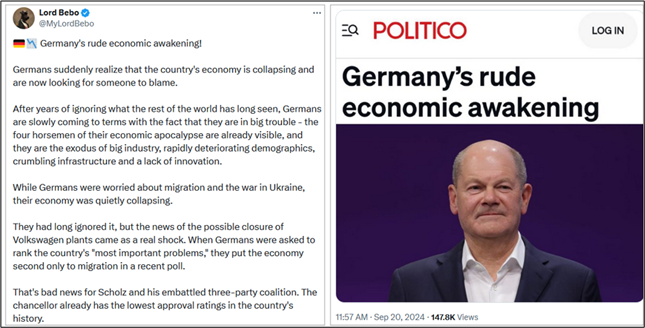
Germany’s rude economic awakening, Politico, September 19, 2024
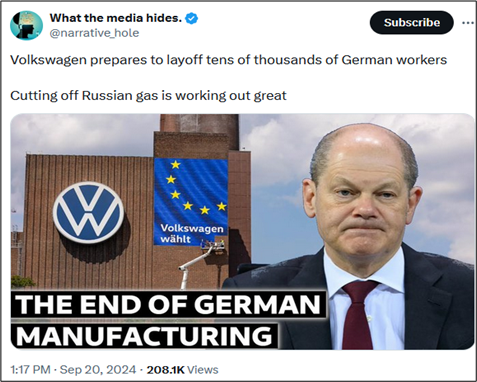
Destruction Of German Auto Industry As Factor For Decline Of EU Economy, the Intel Drop, September 8, 2024
It seems to be easy to make the following conclusion: the EU, Commission – Parliament – other organs of the union altogether, have striven for so suicidal policies that the whole union will face a risk of paralyzing itself and jeopardizing its existence. The role of the EU on the world scene will reduce as a role of pathetic tiny clown.
BRICS and de-dollarization
With less than a month before the crucial BRICS annual summit in Kazan under the Russian presidency, serious discussions and speculations are raging in Moscow and other Eurasian capitals on what should be at the table in the de-dollarization and alternative payment system front. Curiously, the western media seem not to be interested in this topic at all. The background information is available in my article “BRICS overview 2024” of July 22, 2024.
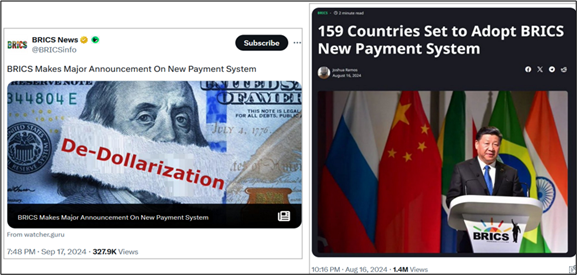
There are a lot of indications / speculations of significant ideas / proposals / plans etc. like digital payment platform (BRICS Bridge), a blockchain-based payment system (BRICS Pay), a settlement depository, an insurance system and a BRICS rating agency. These things will be disclosed in Kazan in late October.
BRICS Meeting to Develop Multipolar World – Jeffrey Sachs, Alexander Mercouris & Glenn Diesen
The Duran, September 19, 2024
🚨BRICS Pay System: Final Development Stage of Blockchain Technology Reached Ahead of the 2024 Summit , Lena Petrova, August 27, 2024
Advisable reading:
De-dollarization the path to global financial freedom
US weaponization of dollar is backfiring as BRICS and wider developing world accelerate away from dollar-based trade and holdings.
Article in Asia Times, by Jan Krikke, August 9, 2024
Tectonic shift coming on global currency markets?
China’s currency could skyrocket if Chinese firms shift their $2 trillion in dollar assets to yuan holdings in response to Fed rate cut
Article in Asia Times, by Nigel Green, August 28, 2024.
The Unite States
On September 18, The US central bank has lowered interest rates for the first time in more than four years with a bigger than usual cut. The Federal Reserve reducedthe target for its key lending rate by 0.5 percentage points, to the range of 4.75%-5%. The move by the Fed follows cuts by other central banks, including those in Europe, the UK, and Canada and a reduction was widely expected.
Jerome Powell, the head of the bank, said the move was “strong” but that it was needed as price rises ease and job market concerns grow. It will be a relief to US borrowers, who have been dealing with the highest interest rates in more than two decades. Wednesday’s cut was larger than many analysts had predicted just a week ago, and the bank’s forecast signaled that rates could fall another half percentage point by the end of the year.
The unemployment rate in the US has climbed to 4.2% from 3.7% at the start of the yearas hiring slowed. Projections released after the meeting showed officials now see inflation falling faster and unemployment rising higher than they did in June, with the jobless rate expected to hit 4.4% by the end of the 2024.The US economy is growing at an annual rate of 3%, the most recent official figures show. Inflation, meanwhile, dropped to 2.5% in August, moving closer to the Fed’s 2% target for the fifth month in a row.
Forecasts released by the Fed showed officials expect its key lending rate to drop to about 4.4% by the end of the year and 3.4% by the end of 2025. That is significantly lower than many were predicting as recently as June.
However, Fed’s performance had a mixed reception. Many financial analysts were thinking: “Cutting rates is a mistake unless they intend to postpone the crash by creating an inflationary bear market. Basically, the market would decline but not crash because commodity speculation prevents it. This is how the Fed postponed 2007 & 2000, which made the recessions far worse.” It remains to be seen what will happen.
Federal debt of the US is just reaching $ 35 trillion and the federal service of the debt goes over 1 trillion yearly level as well as the federal budget deficit. The American debt burden is approaching to “astronomical dimension”.
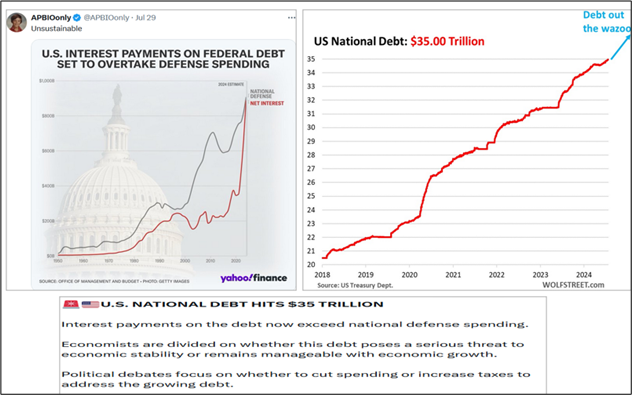
The US is the largest debtor nation in world history and according to the IMF, public debt will exceed 123% of GDP this year and reach nearly 134% by 2029. This means that it will be impossible for the US to overcome its debt. The IMF even recently warned the government about the debt level that will be reached if current policies are maintained. Under current policies, the general government debt is expected to rise steadily and exceed 140% of GDP by 2032.
The Western World, especially the US, has offshored its industrial and manufacturing economy to Asia and Mexico. When the goods and services come into the US to be marketed, they come in as imports, thus enlarging the US trade deficit.
The reason this exploitative system has been able to continue is that after WWII, Washington made the US dollar the means of international payment, that is, the reserve currency of the central banks of the world. Dollar-denominated debt instruments became the reserves of the world’s central banks.
To be the reserve currency means that the country’s debt is the reserves of all other countries’ central banks. Therefore, an increase in US government debt was not a problem, because it meant an increase in reserves of the world’s central banks. This is why financing the US debt was never a problem.
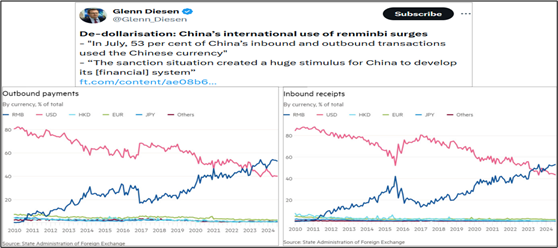
In the 21st century the US government itself has been busy at work destroying this privileged way of financing its ever-growing debt by weaponizing the use of the dollar as reserve currency. The sanctions imposed on Russia and other countries have created a general move away from the use of US Treasury debt as central bank reserves. Washington’s seizure of Russia’s central bank reserves held in dollars told the world that the same could happen to them. Consequently, the use of the US dollar in international payments has fallen from about 90% to a bit less than 50%. With the formation and expansion of BRICS it will fall further.
As other countries cease using the US dollar as their reserves, the implication is a fall in the exchange value of the dollar, already confirmed by the rise in gold and silver prices. In the short run, Washington can prevail on the Japanese, UK, and EU central banks to support the dollar by using their currencies to buy dollars. But this rescue operation of the dollar cannot be forever extended.
The US Government’s Debt Crisis: why bankruptcy is unavoidable and what does it mean
The US government can no longer delay or disguise its impending bankruptcy. The US federal government has the biggest debt in the history of the world and it’s continuing to grow at a rapid, unstoppable pace. In short, the US government can’t repay its debt. It can’t even pay the interest expense without going into further debt. Default is inevitable.
The US government is out of options and cannot repay, what it has borrowed. Therefore, the question is not whether the US government will default but how. That raises an important question: who will buy all this debt (Treasuries)? Historically, there has been a vast foreign appetite for Treasuries but not anymore.
In the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, the US government has launched its most aggressive sanctions campaign ever. The US government and its allies froze around $300 billion of the Russian central bank’s reserves—the nation’s accumulated savings. It was a stunning illustration of the political risk associated with the US dollar and Treasuries. It showed that the US government could deny access to another sovereign country’s reserves at the flip of a switch.
Then, in April 2024, President Joe Biden signed the REPO Act into law. It allows the US government to seize frozen Russian state assets and transfer the funds to Ukraine. In short, the US dollar and Treasuries have become weaponized in a way they had not before. They are now clearly not neutral assets worthy of forming the bedrock of the international financial system but political tools for Washington to coerce others. The rising political risk attached to Treasuries has made them even less attractive as a store of value.
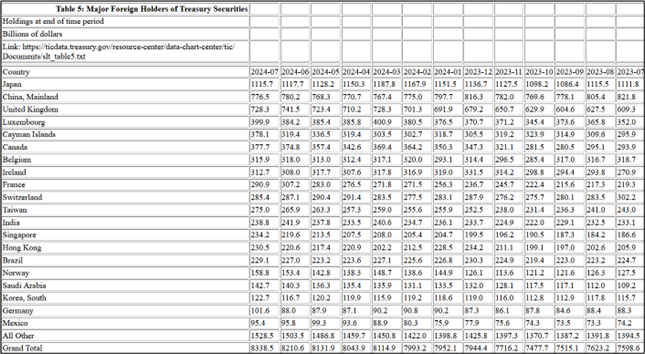
China is one of the largest holders of US Treasuries, and it indeed took note of what is happening. Since 2022—when the US froze Russian state assets—China has sold about 25% of its Treasuries, an enormous change in such a short period. Even US allies, like Japan, have cut their Treasury holdings. The bottom line is that it’s clear the world isn’t hungry for US debt right now as the supply is exploding.
In the bond market, when demand for a bond falls, the interest rate rises to entice buyers and holders. However, the US government cannot allow interest rates to rise because the skyrocketing interest expense has become an urgent threat to its solvency. The interest expense on the federal debt is already bigger than defense spending and is set to become the largest item in the US government’s budget in months.
Thus, who will buy all this debt? The only entity capable of doing this is the Federal Reserve, which buys Treasuries with dollars it creates out of thin air. Here’s the bottom line. The US government can’t pay off its debt. They won’t explicitly default. They can’t entice a meaningful amount of new Treasury buyers by allowing interest rates to rise. That means currency debasement is their only practical option.
Fed Chair Powell’s recent pivot to monetary easing and rate cuts is a symbol of surrendering. That means the Fed has given up on bringing inflation down… even though it remains well above their target. It’s an incredible failure and will have enormous investment implications for the US dollar and gold.
China
In Beijing, there have been speculation that China was about to unleash far more efforts to revive growth, among which further cuts to the country’s Reverse Repo rate and LPR rate but also cuts to the RRR and various other monetary stimulus measures.
That’s precisely what happened, on September 24, when China’s Central Bank (PBoC) Governor Pan Gongsheng unleashed what Bloomberg called a “stimulus blitz” and what some market analysts call “sheer panic”, when he announced a batch of stimulus measures to prop up the sinking economy and crashing stock market. Among these:
- The PBOC will reduce the 7-day reverse repo rate by 20bps.
- The PBOC will cut the reserve requirement ratio by 0.5%, a move that will free up1 trillion yuan ($142 billion) in liquidity
- China may also cut the RRR further this year by another 0.25 to 0.5% at the appropriate time.
- The PBOC will cut the 1 Year MLF rate by 30bps
- The PBOC will also lower the rates for existing mortgages and cut the down payment ratio on second homes to 15% from 25%.
- The deposit rate will be lowered to “neutralize” the impact on bank margins.
“Monetary policy easing come bolder than expected, with both rate cuts and RRR cuts announcing at the same time, we see room for bolder easing ahead in the coming quarters, following the Fed’s outsized rate cuts,” said key analysts.
Moreover, the PBOC governor also said that – in a last-ditch attempt to bail out the country’s stock market – it will set up a swap facility allowing securities firms, funds and insurance companies to tap liquidity from PBOC to buy stocks. Brokers, funds and insurers will be allowed to pledge assets in exchange for liquidity for funds and buy stocks; the PBOC will also set up a separate specialized refinancing facility for listed companies and major shareholders to buy back shares, raise holdings. In other words, Beijing is greenlighting direct intervention in the stock market to prop up stocks.
China has systematically reduced the holdings of US Treasury bonds, being number one for years but now on the second place among foreign investors. Russia has sold out nearly all Treasury bonds. The majority of all treasury bonds is held by the Fed.
Russia
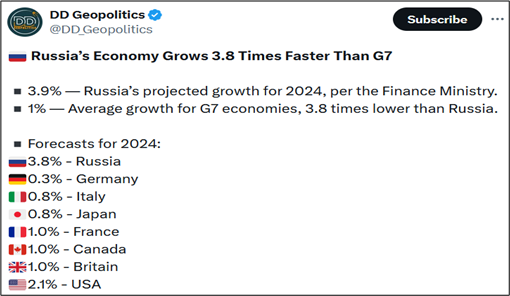
Russia’s gross domestic product (GDP) growth in the third quarter of 2023 was confirmed at 5.5% compared with the same period last year, when it shrunk 3.5%, the state statistics service Rosstat said. Russia’s economy is on course to recover in 2023, 2024 and 2025 while a drop of 2.1% in 2022, as the West imposed sweeping sanctions against Russia over its invasion of Ukraine. Western sanctions regime includes up to 18,000 single sanctions.
In mid-April 2024, IMF has revised upward its estimates of economic development of Russia and forecasts the country’s GDP. According to data presented in the IMF’s report, Russian GDP increased by 3% in 2023, 3.2% in 2024 and over 2% in 2025.
On July 31, according to the estimate of the Russian Ministry of Economic Development, annual GDP in Russia moved up by 3% year on year in June after the rise by 4.5% in May. Overall, GDP moved up by 4.7% year on year in the first half of 2024, according to the estimate of the Ministry.
September 24, Russia’s GDP grew by 4.4% in the first seven months of this year, which is more than two times higher than last year, Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin said at a government meeting.
Positive dynamics was reached due to branches of the real sector, Mishustin noted. “Branches of the real sector were the main drivers. This is first of all manufacturing where output grew by 8.6% in seven months,” he said. “Growth of capital investment closely approached 11% in the first half of the year,” the prime minister said, adding that “the unemployment level has drooped to all-time lows equaling 2.4% this June.”
List of countries imposing destructive attitudes. September 20, Russian Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin approved the list of countries imposing destructive attitudes that contradict Russian spiritual and moral values. The corresponding document has been published. The list includes 47 countries and territories including the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Japan and other EU states. The EU countries that are not included in the list include Slovakia and Hungary, and the NATO countries that are not added to the list include Turkey. The list was approved in accordance with the presidential decree on providing humanitarian support to foreigners who share traditional spiritual and moral values. The order comes into force on the day of its official publication.
July 29, the countries of the collective West have imposed about 20,000 sanctions against Russia’s economy, Deputy Foreign Minister Alexander Pankin told a round table in the Federation Council’s upper house of parliament. “About 20,000 various restrictive sanctions have already been imposed on Russia. Actually, they cannot be called sanctions, because sanctions are a legitimate measure introduced by the UN Security Council, while these are unilateral restrictive measures,” the diplomat said.
Russia boosts use of sanctioned tankers to export its oil. In September, Russia has been using a growing number of oil tankers sanctioned by the West to export its oil, in a move suggesting that Moscow has become more successful in defying US and EU restrictions. A total of six oil tankers sanctioned by the US, the EU or the UK loaded oil cargoes from Russia in August and at least another six have done the same so far in September, according to tanker-tracking data compiled by Bloomberg. The data showed that at least 17 sanctioned tankers have left Russian ports loaded with oil since the end of April. The trend now appears to be accelerating, with mostly tankers owned by Russian state tanker fleet operator Sovcomflot loading cargoes.
Moscow has allowed foreign banks to open branches in Russia and trade for cryptocurrency. Branches of foreign banks will appear in Russia from September 1. On the last day of July, the State Duma adopted in the final reading amendments to the law “On banking activities”, which had been discussed for more than 30 years. The document was initiated by the Russian government and approved by the Central Bank, which will issue licenses for opening branches or refuse to do so. Each foreign bank can open only one branch in Russia.
Wrap-up of economic sphere within next two years
Some conclusions appear to be quite clear and well justified:
- due to massive debt burden, the US economy is facing huge troubles as described above
- after China’s “stimulus blitz”, it remains to be seen, how strong, deep and wide the effects will be on the trajectory of Chinese economy
- Russia’s economy is growing surprisingly strong, despite massive sanctions
- the EU and Europe will face difficult or very difficult times ahead


