Armageddon of US dollar approaching
This article studies the status of US dollar as a reserve currency of international finance and monetary system, significance of SWIFT – financial messaging services as well as the process of de-dollarization run by Russia and China.
The latest information tells that Russia and China are accelerating the de-dollarization process, which will have a fundamental impact on US dollar’s reserve currency status. The fatal process of US dollar will be disclosed in the study below.
Introduction
Ukraine crisis has been a permanent media headline for several months. Biden administration has held nonstop ringing of alarm bells by launching day after day slogans like “imminent Russian invasion” based on unverified US intelligence. Western mainstream media has come along with this intense war mongering. Perhaps some of the readers have been pondering, what is this all about.
On my website, there is the text, which seems to be true, more than ever.
“Welcome to explore the fascinating world of Great Powers. You learn to realize that many things are not what they look like.”
When studying in deeper than just the surface of the present situation, it is possible to understand the particular distress, even the panic, in the US administration. NATO and the EU, not comprehending the essential matter, are enthusiastically messing around with the US.
Regarding the desperation of the US, the real question is neither Ukraine nor even the security arrangement of Europe but simply said the status of dollar and firmly attached to that, the status of the US as a great power. Not less is in question. That’s why the US is also so vehemently opposing Nord Stream 2 pipeline, because in that gas business, euro would be used instead of dollar.
The study below analyzes the whole process (dollar’s status and de-dollarization) ending on future options.
Status of reserve currency
The status of US dollar as the main international reserve currency, after WWII, has been and is today the most important single factor behind the US position as the biggest military force globally. The great power competition and the changes in the polarity of the international system are also due to this matter (base text of this issue, available here).
The reserve currency status has enabled the US to pile up a towering mountain of federal debt of over $30 trillion (in early 2022) — without having to worry about its own financial stability or repayment, at least until now. The US debt-to-GDP ratio is amounting over 130%, bringing the US to the category of “highly-indebted states”.
The process where US dollar reached reserve currency status
The Bretton-Woods System 1946-1971
After WWII the international financial system was governed by a formal agreement, the Bretton Woods System, signed by 44 nations in the conference in Bretton Woods 1944. Under this system the US dollar was placed deliberately as the anchor of the international currency system.
The US Treasury debt replaces the Gold Exchange Standard 1971
The US Treasury kept the dollar’s exchange rate stable by selling gold via the London Gold Pool at $35 an ounce. Finally, in August 1971, President Nixon stopped the drain by closing the Gold Pool and halting gold convertibility of the dollar (so called Nixon shock) and declared the dollar to be a floating currency. The suspension of dollar convertibility marked the end of the Bretton Woods system. Other major currencies became under pressure and finally in early 1973 all became floating.
Birth of petrodollar 1974-1975 and petrodollar recycling
The 1973 oil crisis further fixed the value of the dollar as a result of this oil shock, bringing Saudi Arabia and the OPEC countries to make a secret agreement with Washington, the main architect being President Nixon’s legendary Secretary of State, Dr. Henry Kissinger. In exchange for Washington’s political and military protection, the OPEC countries would be required to sell oil only in dollars. Petrodollar recycling means that oil exporting nations earn more money than they could possibly invest in their own economy and the surplus they shall invest in US debt securities. The term “petrodollar recycling” is coined by Henry Kissinger.
SWIFT
Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) is the Belgium-based worldwide society, the global provider of secure financial messaging services, covering over 200 countries and regions as well 11.000 banks and finance institutions.
After 9/11 terror strike in New York (2001), the US government pressed hard SWIFT Society to allow the American authorities the access into banking data, in order to check, control and curb international currency transactions for terrorist purposes. Finally SWIFT admitted the US authorities the sole access to data and quite soon the US began to utilize it for other purposes as well, namely for politically motivated sanctions.
The US achieved an unparalleled strategic advantage
This dollar status has allowed the US to achieve an unparalleled strategic advantage over its geopolitical opponents (initially the USSR, now Russia and China), namely, a practically unlimited dollar-spending capacity even as it accumulates a skyrocketing public debt (over $30 trillion in early 2022). This has enabled US Government and Pentagon to establish, build up and maintain the military-industrial complex and military forces covering the whole world, “Command of Commons” as Barry Posen expresses this capability.
This “limitless running into debt” has enabled the US nearly “limitless military spending” as well as setting different, politically-motivated sanctions worldwide, according to US political purposes. The US military budget accounts for more than the combined next ten in the world and representing approx. 40% of the world total annually.
The dollar’s role as the undisputed reserve currency of the world as well as the sole access to SWIFT-data, allow the United States to impose unilateral sanctions, threats of trade wars and other punitive actions against any other countries and actors, according to US political will.
The weaponization of dollar and other economic weapons have been frequently used by the US in recent years, e.g. against Russia, Iran, North Korea, Venezuela, China, Cuba, Nicaragua, Turkey, Libya, Syria and a number of other countries (even against the allies) and actors as well. In 2020 the US was at odds with the majority of the humanity worldwide.
However, after the world financial crisis of 2008-2010, the process of de-dollarization began to get more pace in the world economy. As previously turned out, de-dollarization process also entails political and military significance.
De-dollarization scheme, by Russia and China
By far, this joint scheme is the most serious and powerful endeavour to depose the US dollar from the throne, although there have been some other measures before.
Russia’s national measures
Official de-dollarization plan of the Russian economy, 2018 – 2024
In September 2018, Russia’s VTB Bank President Andrey Kostin unveiled his four-part plan to abandon the US dollar in Russia’s transactions with foreign states. The head of the Russian Lower House Committee for Financial Markets, MP Anatoly Aksakov, backed a plan to completely stop using the US dollar, noting that the program can be completed in three to five years. Russian Finance Minister Anton Siluanov said in October 2018, that the plan on de-dollarization of the Russian economy had already been prepared and submitted to the government. According to the plan, Russia seeks to fully de-dollarize the economy by 2024.
The program is complicated but the key point is that Russian exporters, who use rubles instead of dollars would get huge taxation benefits including quicker VAT returns and other stimulus to ditch the dollar. Russia will gradually switch to such a system of international payments, which implies payment in rubles for Russia’s goods on the world market like oil, gas and arms exclusively. Russia is going to create a new payment system (SPFS) that cannot be controlled by the US (the alternative to the SWIFT). This system’s development was started in 2015 and has been in test use since 2017.
Russia’s growing forex reserves and low debt
Russia’s gold purchases have been at record high level in last five years making Russia as the biggest purchaser and the fifth biggest holder of monetary gold in the world. There has been a strong shift from US dollars to euros, yuans and yens in the assortment of foreign currencies held by Russian Central Bank. Russia liquidates nearly all its holdings of US treasury bonds and other US debt and invested money in gold. Total amount of forex reserves exceeded $ 620 billion in late autumn 2021 ranking Russia as the fifth in the world. Russia’s public debt-to-GDP-ratio is about 17% making one of the lowest debt-ratio states in the world. A balanced or surplus state budget is another reason, why Russia does not need to borrow abroad.
Central Bank of Russia (CBR) has kept the principle “the smaller the debt, the lesser the chances of a default.” The key basic rationale behind “the policy of the low debt and high buffer reserves & just moderate economic growth” is the deliberate and willful endeavour to “teflonize” the Russian national economy against outside sanctions and other punitive measures. The strategy is designed to avoid a repeat of 2014 when the West imposed sanctions on Moscow and the ruble to plunge.
China’s national measures
The ongoing trade conflict between the US and China as well as sanctions against Chinese entities have forced China to take steps towards relieving the dollar dependence of the world’s second-largest economy. The Chinese government has not made any loud announcements on the issue. However, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) has been regularly reducing the country’s share of US Treasuries, being still number-two foreign holder of the US sovereign debt. China like Russia started to develop its own foreign payment platform (CIPS), which is a competing system vs. SWIFT. The test use has been going since 2019.
Moreover, instead of promptly dumping the dollar, China is trying to internationalize its own currency, the yuan, which was included in the IMF basket alongside the US dollar, the Japanese yen, the euro, and the British pound. Beijing has recently made several steps towards strengthening the yuan, including accumulating gold reserves, launching yuan-priced crude oil futures and using the currency in trade with international partners. China is officially launching a digital yuan during the Olympic Games 2022, which is obviously a part of yuan’s internationalization agenda. Digital yuan has become quickly very popular, over 140 million personal wallets have been opened by the end of 2021 in China.
As part of its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China is planning to introduce swap facilities in participating countries to promote the use of the yuan. Moreover, China is actively pushing for a larger use of yuan and national currencies in the context of the agreement called the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), which include the countries of Southeast Asia. RCEP includes 16 country signatories and form a union of nearly 3.4 billion people based on a combined $50 trillion economy, which accounts for nearly 40 percent of the world’s GDP.
Within the framework of other multinational associations, like BRICS, SCO and EAEU, as well as in bilateral trades, both China and Russia are purposefully aiming at use more and more of national currencies instead of US dollars. This procedure is in use already in the trade with India, Iran, Turkey, the EU, Japan and numerous African countries.
Recent statements regarding de-dollarization
Amid a worsening stand-off between East and West, Russia and China are increasingly contemplating using their own currencies in mutual settlements and finding ways to work together to counter sanctions, Moscow’s envoy in Beijing has disclosed in early February 2022. Andrey Denisov weighed in on the impact of embargoes imposed by Western nations on ties between the two nations. According to the envoy, “it is no coincidence that in recent years we have been talking more and more about the wider use of national currencies in the settlement of foreign trade transactions.”
In December, President Vladimir Putin’s foreign policy advisor, Yuri Ushakov, revealed that the Russian leader and his Chinese counterpart, Xi Jinping, had vowed to develop shared financial structures to enable the two nations to deepen their economic ties, without the interference of third countries. The move appeared to be a response to a series of warnings from the West that Moscow could be cut off from the Brussels-based SWIFT international payment system as a punitive measure if Russian troops were to stage an invasion of Ukraine.
Last year, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov said that the two nations “need to move away from the use of Western-controlled international payment systems.” His remarks echoed earlier comments from his deputy, Sergey Ryabkov, who told the Bloomberg business news outlet that it was necessary to “barricade ourselves against the US financial and economic system to eliminate dependence on this toxic source of permanent hostile actions,” and “cut back the role of the dollar in any operations.”
In a signed article by President Putin titled “Russia and China: A Future-Oriented Strategic Partnership” was published by Xinhua News Agency on Thursday, February 3, 2022: “We are consistently expanding settlements in national currencies and creating mechanisms to offset the negative impact of unilateral sanctions. A major milestone in this work was the signing of an agreement between the Government of Russia and the Government of China on payments and settlements in 2019.”
Joint Payment Platform System, by China and Russia, December 2021
In the recent video summit Putin – Xi December 15, 2021, Russia and China promised to develop new shared financial structures to enable the parties to deepen economic ties in a way that foreign states will be unable to influence. The payment platform underpins the vast majority of international transactions. The development work of substituting SWIFT-system by some joint Sino-Russian system has been going in both countries since 2015 (Russian SPFS and Chinese CIPS).
During the December 2021 talks, Putin and Xi called for increasing the share of national currencies in mutual settlements and expanding cooperation to provide Russian and Chinese investors with access to their stock markets. Both Russia and China are increasingly moving away from using the US dollar as the main currency of international trade, instead using their own denominations to underpin the booming volume of Moscow-Beijing trade. This trajectory is now accelerating, the share of dollar was about 90% in 2015 and in 2021 a bit over 40% in their bilateral trade.
Russia – Iran summit, January 2022
The Russia – Iran summit in late January 2022 in Russia, concurrent with Russia-Iran-China navy drills in the Sea of Oman, in advance of Xi-Putin meeting in early February in Beijing, suggests a rapidly-advancing strategic vision for the three Eurasian powers.
The key topic on the agenda was “a document on strategic cooperation” between Iran and Russia. The road map document will be the base for the new 20-year strategic partnership agreement, which will be finalized, obviously in 2022. This procedure is, in fact, an update of a previous 20-year cooperation treaty signed in 2001, originally meant to last for 10 years and then twice extended for five years.
A key item of the new 20-year strategic partnership between the two neighbors is bound to be a Eurasian-based clearing network designed to compete with SWIFT, the global messaging system between banks. Once the system is up and running, obviously in 2022, that’s perfect for Iran, which badly wants to increase trade with Russia but remains handicapped by US sanctions. Iran has already signed trade agreements and is involved in long-term strategic development with both Russia and China.
China – Russia Summit in Beijing, February 4, 2022
President Xi Jinping and his counterpart Vladimir Putin held talks in Beijing and took part in the opening ceremony of the XXIV Olympic Winter Games. The joint statement was published, based on their talks.
Both Russia and China oppose interference in their internal affairs, which is in accordance with all Westphalian principles. Important component of that drive was to consistently expand the role of national currencies and maintaining mechanisms to offset the impact of unilateral United States sanctions. This is very important point.
The US has consistently used the central role of the US dollar in international trade as a vehicle for affecting the national policies of the countries forced to use the dollar. That is now changing and the pace of change is expected to grow in the forthcoming years as more and more countries abandon the dollar as the means of international trade payments.
There was no detailed reference to the de-dollarization in the Joint Statement but some points in the document are relevant in this respect:
The sides are seeking to advance their work to link the development plans for the Eurasian Economic Union and the Belt and Road Initiative with a view to intensifying practical cooperation between the EAEU and China in various areas and promoting greater interconnectedness between the Asia Pacific and Eurasian regions. The sides reaffirm their focus on building the Greater Eurasian Partnership in parallel and in coordination with the Belt and Road construction to foster the development of regional associations as well as bilateral and multilateral integration processes for the benefit of the peoples on the Eurasian continent.
The sides support the deepened strategic partnership within BRICS, promote the expanded cooperation in three main areas: politics and security, economy and finance, and humanitarian exchanges. In particular, Russia and China intend to encourage interaction in the fields of public health, digital economy, science, innovation and technology, including artificial intelligence technologies, as well as the increased coordination between BRICS countries on international platforms.
The sides will contribute to imparting a new quality and dynamics to the economic interaction between the SCO member States in the fields of trade, manufacturing, transport, energy, finance, investment, agriculture, customs, telecommunications, innovation and other areas of mutual interest, including through the use of advanced, resource-saving, energy efficient and green technologies.
No doubt these points refer to the extensive user base of the coming “SWIFT-alternative”.
Cutting off Russia from SWIFT
With increasing talks in the US and European Union about cutting off Russia from the global SWIFT network as a “sanction from hell” due to Russian invasion in Ukraine (or Russian military buildup threatening Ukraine), the question returns to the alternative networks Russia can employ.
The SPFS is the Russian equivalent of SWIFT and has been under development by the Central Bank of Russia since 2015, after the United States government threatened to disconnect Russia from the SWIFT system.
The first transaction on the SPFS network involving a non-bank enterprise was executed in December 2017. As of March 2018, over Russian 400 institutions (mostly banks) are part of the network meaning that the SPFS system supports intra-Russian transactions. However, the problem with any SWIFT disconnection would be the absence of international connectivity. That becomes a question as to how quickly Russia is able to integrate SPFS with other systems and whether or not the United States would also place sanctions on countries connecting to SPFS.
While Russia’s SPFS can be three times cheaper than SWIFT, the present network itself is only operational during weekday working hours and its messages are limited to 20kb in size. SWIFT, meanwhile, works 24/7 and allows 10mb to be transmitted across its network.
There is now the plan to integrate the Russian SPFS network with the China-based Cross-Border Inter-Bank Payments System (CIPS), while the Russian government is also in talks to expand SPFS to other countries such as Turkey and Iran. Since 2019 many agreements have also been reached to link SPFS to other countries payment systems in China, India, Iran, as well EAEU-countries Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan. The EAEU also has Free Trade Agreements with Serbia, Singapore and Vietnam with multiple other deals pending. At the end of 2020, 23 foreign banks connected to the SPFS from Armenia, Belarus, Germany, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Switzerland.
The stakes in disconnecting Russia are high and would certainly increase the risk of Russia’s invasion in Ukraine and gradually bring its economy into the Eurasian Economic Union. It would escalate a new Cold War with mutually disconnected systems. EU trade and energy from Russia would be put in jeopardy and should be replaced by the United States instead, meaning EU consumer prices would significantly increase.
Perhaps in advance warning of further trouble ahead, Belarus, which borders both Russia and Ukraine, has begun the process of disconnecting its own financial systems from the SWIFT network and connecting them instead to Russia’s System for Transfer of Financial Messages (SPFS) alternative.
An additional unknown factor is, exactly how fast and how extensively the Russian SPFS system can be integrated with other systems such as China’s CIPS.
Chinese Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS)
Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) is a payment system, which offers clearing and settlement services for its participants in cross-border RMB payments and trade. It is a significant financial market infrastructure in China. In October 2015, CIPS Phase I development went live. The first batch of direct participants included 19 Chinese and foreign banks and 176 indirect participants in 47 countries and regions. In March 2016, CIPS signed an MoU with SWIFT of deploying SWIFT as a communication channel for CIPS’s connection with SWIFT’s members.
CIPS would not facilitate funds transfer, it sends payment orders, which must be settled by correspondent accounts that the institutions have with each other. Each financial institution, to exchange banking transactions, must have a banking relationship by either being a bank or affiliating itself with one (or more) to carry out enjoy those business features.
However, it was reported in July 2015 that CIPS development would be reduced for cross-border yuan trade deals only rather than including capital-related transactions. Also, some technical problems delayed the project. Today CIPS may offer a complementary network for settling trade-related deals in the Chinese currency.
Joint Payment Platform System, by China and Russia
In the recent video summit Putin – Xi December 15, 2021, Russia and China promised to develop new shared financial structures to enable the parties to deepen economic ties in a way that foreign states will be unable to influence. The payment platform underpins the vast majority of international transactions. The development work of substituting SWIFT-system by some joint Sino-Russian system has been going in both countries since 2015 (Russian SPFS and Chinese CIPS).
The move appears to be a response to a series of recent warnings that Western nations could push to disconnect Russia from the Brussels-based SWIFT financial system as a form of sanctions. When this new joint system will be available, no doubt, a large number of other countries will join in as well. The most important banks in both countries will adopt the system – as well as banks across Eurasia and Asia doing business with them and then a large number of the Global South banks. SWIFT, in the long run, will be used only in exceptional cases, if China and Russia have their way. Therefore, particular attention was paid to the need to further intensify efforts to form an independent financial infrastructure to service trade operations between Russia and China, which means creating an infrastructure that cannot be influenced by third countries.
Obviously, the purpose of this Sino-Russian joint project is to create a Eurasian-based clearing network designed to compete with SWIFT, the global messaging system between banks. Starting with Russia, Iran and China (RIC), this mechanism has the potential to unite member-nations of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), the Eurasia Economic Union (EAEU), ASEAN, BRICS and other regional trading/security organizations. The combined geo-economic weight of all these actors will inevitably attract many others across the Global South and even Europe.
The basis for this already exists. China launched its Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) in 2015, using the yuan. Russia developed its System for Transfer of Financial Messages (SPFS). To build an independent Russian-Chinese financial system by linking the two existing national systems should not be an insurmountable problem, so much top-level expertise is available in both countries. One question is to choose the standard currency – possibly the yuan.
Once the new system is up and running, obviously sometimes in 2022, that is also perfect for Iran, which badly wants to increase trade with Russia but remains handicapped by US sanctions. Iran has already signed trade agreements and is involved in long-term strategic development with both Russia and China.
Economic position of the US, the latest info
Dollar’s central role in world financial markets has reflected both faith in American leadership and the absence of reasonable alternatives. This role now faces extensive and escalating risks. One sign is the weakening faith in America’s ability to hold the system together.
US indebtedness has been for four last years at very alarming level, federal debt exceeding $30 trillion in early 2022 and all other sectors in American society also at record high debt levels. Federal budget deficit exceeds now a trillion per fiscal year 2021 and is enlarging. Imbalance between the incomes and expenditures is staggering, especially the military expenditures seem to be overwhelming.
US trade deficit in both goods and services rose to a record $859 billion in 2021 as imports surged, the US Commerce Department has reported. US imports rose by 20.5 percent to $3.39 trillion in 2021 while exports climbed by 18.5 percent to $2.53 trillion, according to the department.
The US economy grew 5.7 percent in 2021, mainly due to the massive fiscal and monetary support packages by Biden administration (100% debt financing), following a pandemic-induced contraction of 3.4 percent in 2020, according to the department. Rising inflation is also playing a growing role in the US economy. The US consumer price index rose 7.5 percent in January from a year earlier, the largest 12-month increase for 40 years.
The future of US dollar and its role in financial diplomacy
Although the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has served as the world’s principal forum for the promotion of international monetary cooperation and maintains an essential tool kit for this purpose (SDR and affiliated Funds), the Fund has not been fully able to cope with the deficiencies of the present dollar-based system. In the context of worldwide finance crisis in autumn 2009, the UNCTAD issued a report calling for a new reserve currency based on the SDR, managed by a new global reserve bank. The IMF released a report in February 2011, stating that using SDRs could help stabilize the global financial system.
Power and status of reserve currency ultimately depends on trust in the intentions of the issuer
The US and its military and political allies have had long negotiation processes for decades to create present monetary and financial policies and institutions. While the power of the US military has been able to force “Pax America” worldwide, so the US Federal Reserve and Treasury have played pivotal roles in stabilizing financial markets.
But now… historical transformation is taking place and the demise of the US dollar seems to be inevitable. Both internal and external factors, as studied in the section What If, Part 2 are telling frightening but realistic way the irreversible downfall of the American society as well the US dollar.
Overwhelming majority of present Western economists and other economic pundits have not been able or willing to comprehend or accept such a possibility that the present status of international reserve currency (the US dollar) could somehow downfall, not to mention the collapse.
The Sino-Russia joint scheme of de-dollarization has been left nearly totally unnoticed by Western researchers. Consequently, the life of any fiat money, including reserve currencies, has not been so long as seen in the picture below.
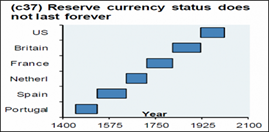
What will happen next?
As stated above, in the video summit December 15, 2021, Putin and Xi promised to develop Sino-Russian Joint Payment Platform System (SWIFT-alternative) and increase significantly national currencies in their bilateral trade and also in their international trade.
The purpose of this Sino-Russian joint project is to create a Eurasian-based clearing network designed to compete with SWIFT, the global messaging system between banks. Starting with Russia, Iran and China (RIC), this mechanism has the potential to unite member-nations of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), the Eurasia Economic Union (EAEU), ASEAN, BRICS and other regional trading/security organizations. The combined geo-economic weight of all these actors will inevitably attract many others across the Global South and even Europe.
When this new platform will be released, obviously in 2022, it has thorough-going, fundamental consequences and ramifications, not only in the currency market but in the whole balance of power among great powers. All premises will be shaking.


